Co Op Living Communities: In-Depth Guide to Shared Housing, Benefits, and Real-Life Examples
The way people live in cities is evolving. Rising housing costs, growing urban populations, and the desire for meaningful social connections are reshaping how individuals think about home. One increasingly popular solution is co op living communities. These communities offer more than just shared housing; they represent a new lifestyle built on cooperation, affordability, and collective well-being.
This article explores the concept of co op living communities in detail. We will discuss what they are, how they function, their benefits, and provide real-world examples to help you understand why they are becoming a vital part of modern urban living.
What Are Co Op Living Communities?
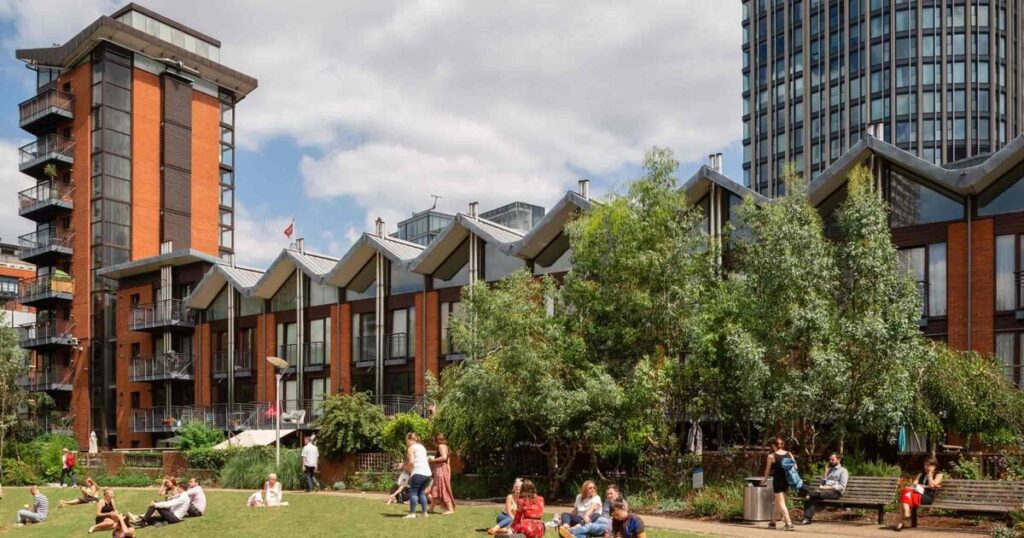

Co op living communities, short for cooperative living communities, are residential spaces where people come together to share housing, responsibilities, and resources. Unlike traditional apartments or rental homes, residents in co op living often manage their communities collectively.
The model is built around cooperation and shared decision-making. Each resident typically has a private room or unit while sharing common spaces such as kitchens, lounges, and gardens. Residents often contribute time or resources to help maintain the property, organize events, or manage utilities. This structure promotes affordability, sustainability, and social interaction.
Why Co Op Living Communities Are Growing in Popularity

Several factors explain why co op living communities are gaining momentum:
- Affordability: With housing costs rising globally, co op communities allow people to share expenses and live in better conditions at lower costs.
- Community: Many individuals face loneliness in cities. Co op living fosters social connections and creates a sense of belonging.
- Sustainability: Shared resources reduce waste and encourage eco-friendly lifestyles.
- Flexibility: These communities can serve students, professionals, families, or retirees, depending on the design.
Together, these factors make co op living a practical and appealing alternative to traditional housing.
Core Features of Co Op Living Communities
Shared Resources and Responsibilities
A key element of co op living is resource sharing. This includes not only physical spaces such as gardens, kitchens, and living rooms, but also utilities, appliances, and tools. By pooling resources, residents reduce costs and consumption.
Responsibilities are also shared. Maintenance, gardening, or organizing community events often rotate among members, ensuring everyone contributes to the functioning of the community.
Decision-Making and Governance
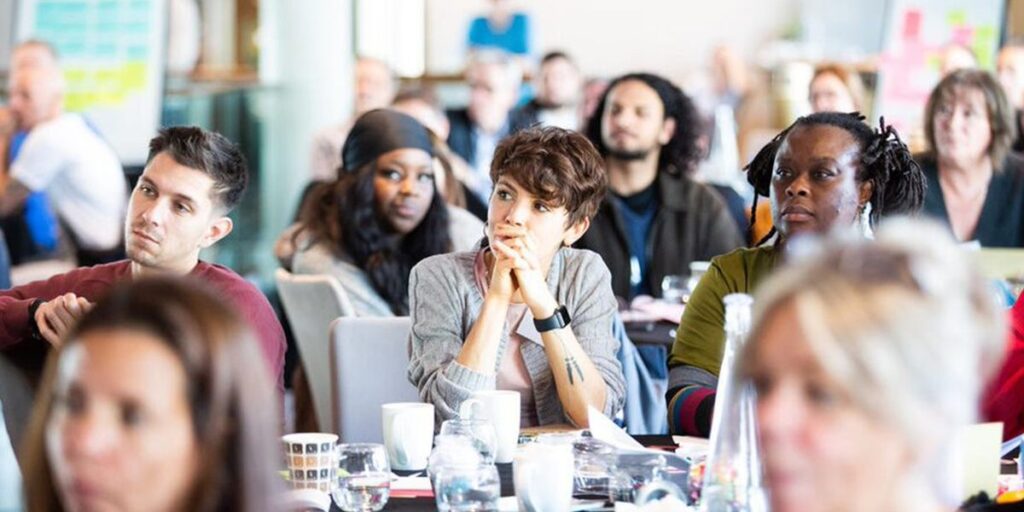

Unlike rental housing managed by landlords, co op living communities often use democratic decision-making. Residents may hold regular meetings to decide on budgets, activities, or rules. This collaborative approach ensures everyone’s voice is heard and creates a deeper sense of ownership.
Governance models may vary, but they all center on transparency, participation, and cooperation. This makes co op living distinct from both traditional renting and typical shared apartments.
Technology Integration
Modern co op living communities are increasingly supported by technology. Apps and digital tools are used for:
- Managing schedules and responsibilities
- Tracking utility use and expenses
- Organizing community events
- Communicating between members
Technology reduces friction in daily management and helps communities run more smoothly. It also enhances transparency in decision-making.
Real-World Examples of Co Op Living Communities
To better understand the versatility of this model, here are real-world examples of how co op living communities are designed and function.
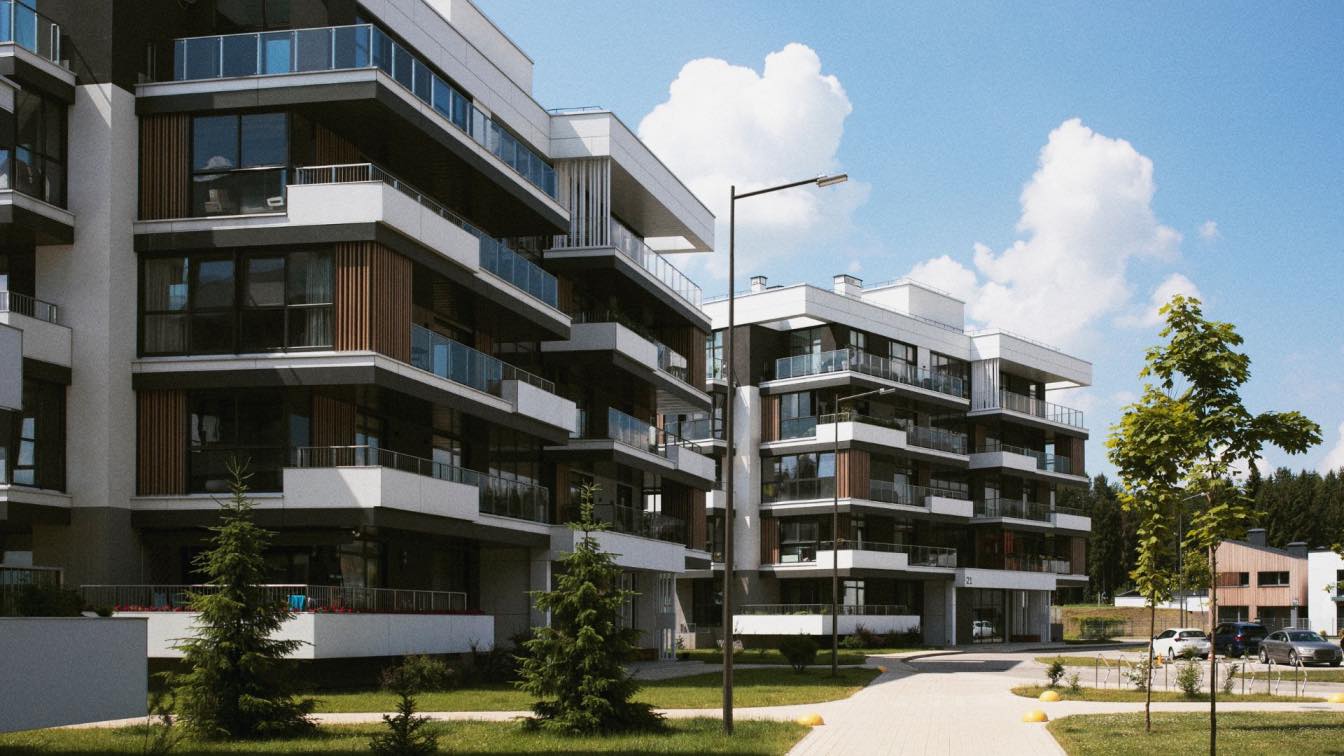
Urban Co Op Housing

Urban co op living is common in cities where housing prices are high. Residents live in shared apartment complexes, pooling rent and resources to reduce costs. These communities often include shared kitchens, coworking areas, and rooftop gardens.
They cater to professionals and students who want affordable housing while enjoying a central location. Events such as shared dinners, workshops, and cultural activities make urban co-ops vibrant social hubs.
Student Co Op Living
Many universities and towns have student housing cooperatives. These co-ops are managed by students who share cooking, cleaning, and budgeting tasks. The system teaches responsibility, financial management, and cooperation while significantly lowering living costs.
Beyond affordability, student co-ops provide strong peer support networks, making academic and social life more balanced and enjoyable.
Eco-Focused Co Op Communities
Some co op communities are built around sustainability. These eco-focused communities use renewable energy, organic gardens, and shared transportation like bikes or electric cars.
Residents actively participate in reducing their environmental impact. This model appeals to individuals who prioritize eco-friendly living and want to align their housing with their values.
Senior Co Op Living
Co op living is not only for students and professionals. Senior co op communities allow older adults to live independently while still enjoying social support. These communities provide accessible housing, shared healthcare services, and group activities designed for seniors.
This setup helps reduce isolation among older adults and creates a safe, supportive environment for aging with dignity and companionship.
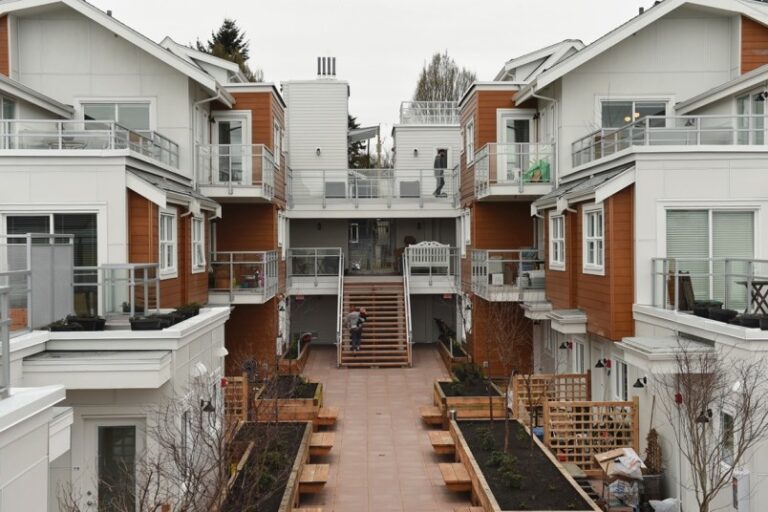
Family-Oriented Co Op Communities
Family-orientedco-opss are designed to support households with children. Shared play areas, childcare arrangements, and community kitchens make family life more manageable. Parents often collaborate on school runs, childcare, and extracurricular activities, reducing stress and costs.
This model provides families with a supportive network, allowing them to raise children in a safe, cooperative environment.
Benefits of Co Op Living Communities
The advantages of co-op living, family-oriented, co-op savings:
- Economic: Lower housing costs, shared expenses, and fewer financial risks.
- Social: Reduced loneliness, stronger support networks, and increased collaboration.
- Environmental: Lower resource consumption and more sustainable lifestyles.
- Educational: Residents often learn valuable skills in governance, budgeting, and teamwork.
- Health and Well-being: Access to community activities and shared wellness programs.
These benefits explain why co op living is considered both a lifestyle choice and a practical housing solution.
Problems Solved by Co Op Living Communities
Co op living communities address many challenges in modern housing:
- High rent costs: By sharing housing, residents access affordable living in expensive cities.
- Isolation: Co-ops encourage social interaction, reducing loneliness.
- Sustainability: Resource sharing reduces energy use and waste.
- Limited housing options: Co-ops provide flexible models for students, families, or seniors.
- Management transparency: Democratic decision-making empowers residents to control their environment.
In each case, co op living proves to be more than just housin;g it is a solution to broader societal challenges.
The Role of Technology in Co Op Living
Technology continues to transform co op living communities. From scheduling chores to managing budgets, apps streamline daily operations and prevent conflict. Smart energy systems help track usage and lower costs, while communication platforms strengthen community bonds.
As more communities embrace digital tools, co op living becomes not only more efficient but also more attractive to younger, tech-savvy residents.
Why Co Op Living Communities Represent the Future of Housing
The rise of co op living communities reflects a broader trend toward collaboration, sustainability, and affordability in housing. As urbanization increases and people seek meaningful social connections, co op models provide an adaptable solution.
They combine the strengths of community living with modern technology, creating spaces that are inclusive, affordable, and resilient. For many, co op living is not just a practical option but a vision of a better way to live.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How is co op living different from regular shared housing?
In co op living, residents not only share spaces but also participate in collective decision-making and responsibilities. It is more structured and community-driven compared to informal shared apartments.
Q2: Who can join a co op living community?
Co op communities can serve a wide range of people: students, professionals, families, and seniors. Each community typically defines its focus and admission guidelines.
Q3: Are co op living communities sustainable?
Yes. By sharing resources and encouraging eco-friendly practices, co op communities significantly reduce waste, energy consumption, and environmental impact.